71 Animal Organ System Definition
Plant life and animal life rely on many organs that co-exist in organ systems. Humans and other mammals have many organ systems.
A given organs tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma the tissue peculiar to or at least archetypal of the organ and that does the organs specialized job and stroma the tissues with supportive structural connective or ancillary functions.
Animal organ system definition. Here are some organ systems common to most animals including humans. Homeostasis is a term coined in 1959 to describe. The thoracic which contains the heart and lungs.
Organ systems such as the digestive system are collections of organs that perform a major function for the organism. The head or cephalic region contains four of the five senses as well as a brain encased in the bony skull. An organ system is a group of organs that work together to perform a certain function in an organisms body.
It is the most complex organization in your body and the final level of the progression from cells to tissues to organs and then systems. Systems work alone and. The organ systems of animals are groupings of organs that work together.
Major organs in this system are the Trachea Bronchi Bronchiole tubes Lungs and Alveoli. Homeostasis Back to Top. The vertebrate body has two cavities.
Animal Organ Systems Anatomy and Physiology. Organ systems are groups of organs that work together to perform a specific function. A system is a group of organs that work together and provide an organism with an advantage for survival.
Animal organ systems. Stems and leaves are two types of organs found in plants. Eleven major organ systems are present within animals although some animals lack one or more of them.
These organ systems can be grouped according. Tissues are made from cells of a similar type. Supplies O2 to the cells and removes CO2.
Most animals and plants have organs which are self-contained groups of tissues such as the heart that work together to perform one function. A body system consists of a number of organs which work together to carry out. 12 rows A group of tissues or organs often with a common embryological origin that.
These changes might be in the level of glucose or calcium in blood or in external temperatures. Exchange of O2 and CO2 between an organism and its external environment. The nervous system cardiovascular system.
Cells need oxygen foodenergy and water to survive. Animals from mice to monkeys have the same organs heart lungs brain etc and organ systems respiratory cardiovascular nervous systems etc which perform the same functions in pretty much the same way. And the abdominal which contains digestive organs.
Fundamentals of Life All living things are made up of cells. An organ is a group of tissues with similar functions. The stomach is involved only in the digestion of food as part of the digestive system.
Organs are made from tissues and systems are made from several organs working together. In biology an organ is a structure composed of a group of different tissues that work together to perform a specific function. Most organs have functions in only one organ system.
An example of an organ system is the circulatory system which includes the. It has a special job or jobs to do. The stomach liver lungs and heart are examples of organs found in animals.
An organ is a complex structure within the body. Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment. Examples include skeletal muscular nervous digestive respiratory reproductive endocrine circulatory and urinary systems.
Cells are the most basic structure of life. Most multicellular organisms have one or more organs. Animals and plants are made of cells.
Organs examples of which include lungs kidneys hearts and spleens are groups of several tissues that function together. Animal organs and organ systems constantly adjust to internal and external changes through a process called homeostasis steady state.
42 Animal Reproduction Diagram
Fill up the conceptual diagram about animal reproduction - 9865554 marloumarciales marloumarciales 27012021 Science Junior High School answered Fill up the conceptual diagram about animal reproduction 1 See answer zyrenerojo2004 zyrenerojo2004 Answer. Fusion of gametes takes place to give rise to offspring.
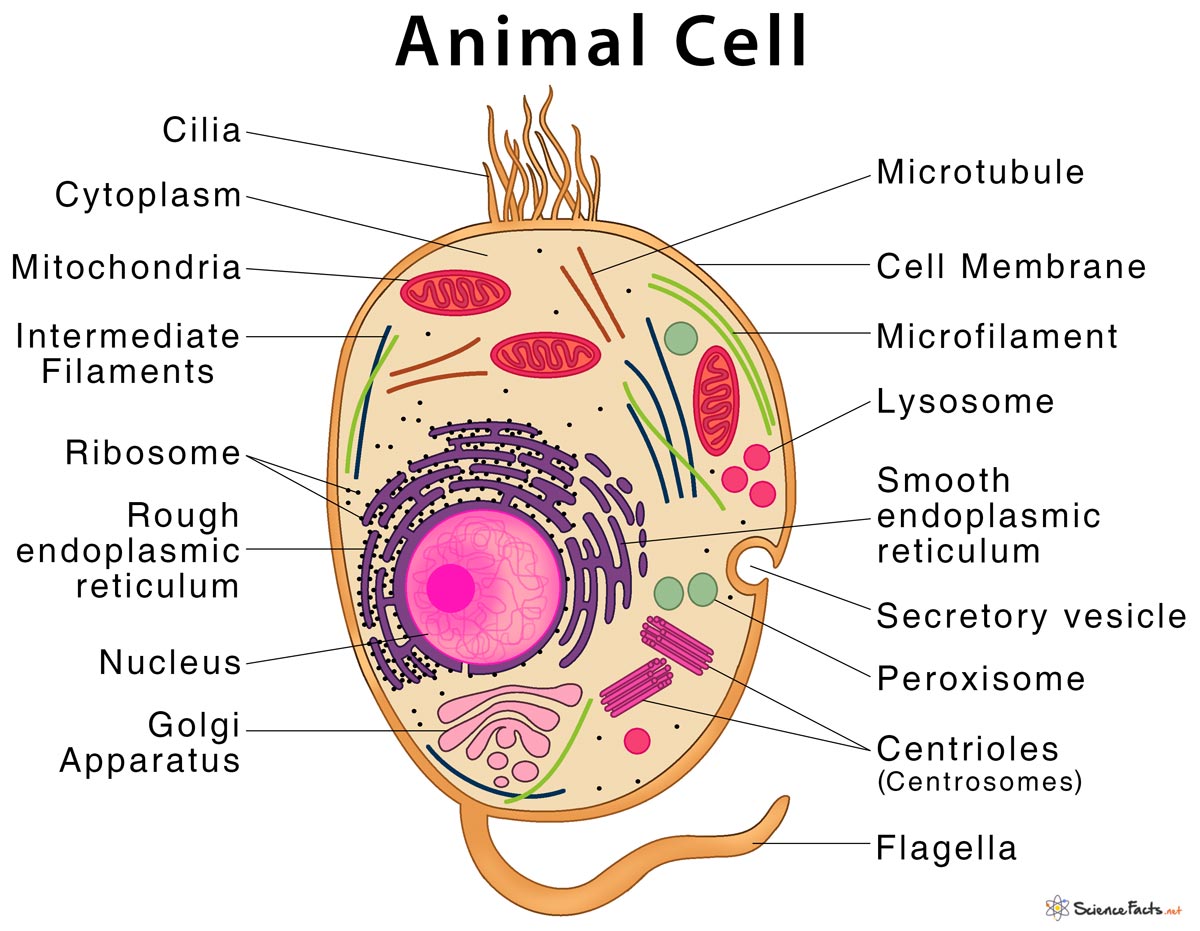
Animal Cell Structure Parts Functions Types With Diagram
Identify and describe the mal e reproductive organs in cattle.

Animal reproduction diagram. 1 megasporangia of each ovule divides by meiosis- produces 4 megaspores in which the last surviving becomes the female gamete. In amphigony two gametes fuse to form a zygote. During puberty the hypothalamus in the brain signals the pituitary gland to produce two hormones follicle-stimulating hormone FSH and luteinizing.
Animal Reproduction Science publishes results from studies relating to reproduction and fertility in animalsThis includes both fundamental research and applied studies including management practices that increase our understanding of the biology and manipulation of reproduction. In sexual reproduction there is involvement of two parents that generate gametes. It requires various physical and behavioral transformations which are controlled by hormone production and other factors.
Useful notes on Asexual Reproduction and Sexual Reproduction are described below. The lower animals like protozoans sponges and few coelenterates reproduce in one simple way while all the rest follow a different pattern of reproduction. There are about 12 million types of animals.
Explain that while this diagram is of a cows reproductive system the females of most species of mammals have similar parts. A species may have separate sexes or combined sexes. These gametes may be from same parent or different parents.
There are two types of sexual reproduction in animals. Fibrous coat surrounding and protecting the testis. Animal Reproduction Jason Gehrke 3025A 3025M 3025N 2.
We were unable to load the diagram. Seminiferous tubules in which the sperm are made. Some animal speciesincluding sea stars and sea anemonesare capable of asexual reproduction.
ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Block Diagram Use Createlys easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. Collecting ducts where the sperm are stored. Uncover the diagram of the reproductive tract of a cow.
Colour and label the structures in the diagram. Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives. Asexual reproduction in animals occurs through fission budding fragmentation and parthenogenesis.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives. 2 In the microsporangium of the anther microspores form the pollen.
The diagram below shows a sperm. Animal reproduction is an important aspect of many 4-H animal science projects but lessons on the subject. Tap diagram to zoom and pan.
Epididymis in which sperm mature and become motile. For animals to reproduce they need to reach sexual maturation. Start studying Animal Sexual Reproduction.
Sexual Reproduction in Animals. There is a large diversity among animals. This process produces a diploid fertilized egg called a zygote.
Vas deferens or sperm duct. Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 1. The role of reproduction is to provide for the continued existence of a species.
The most common forms of asexual reproduction for stationary aquatic animals include budding and. Animal reproduction is a complex and varied set of processes which all have the same goal. You can edit this template and create your own diagram.
Typically both male and female gametes are required. Animal reproductive system any of the organ systems by which animals reproduce. Manuscripts should go into depth in the mechanisms involved in the research reported rather than give a mere.
Sexual reproduction may involve fertilization inside the body or in the external environment. Animals compete with other individuals in the environment to maintain themselves for a period of time sufficient to enable them to produce tissue nonessential to their. Diagram of major female reproductive organs Image modified by Khan Academy from OpenStax CC BY 40 Humans females become capable of reproduction at sexual maturity which follows puberty.
It is the process by which living organisms duplicate themselves. Hormones Male Testosterone- critical for sperm development Female Estrogen- critical for follicle development Progesterone- sustains pregnancy and inhibits new follicle development Relaxin- causes ligaments around birth canal to relax Oxytocin- causes milk letdown. The small motile male sperm fertilizes the typically much larger sessile female egg.
When the sexes are combined they may be expressed at different times in the life cycle. Animal reproduction 1.

